Barcode 101: What You Need to Know About Barcode
Barcodes are an integral part of modern life, yet many of us overlook their significance. They are far more than just the lines or modern 2D grids on product packaging. Barcodes offer numerous benefits and conveniences, from streamlining business operations to enhancing the shopping experience for consumers. For businesses, they are a powerful tool for inventory management, cost control, and supply chain optimization. For consumers, they simplify the checkout process and provide access to product information. Understanding barcodes is essential in today's fast - paced, technology-driven world.
What is a Barcode?
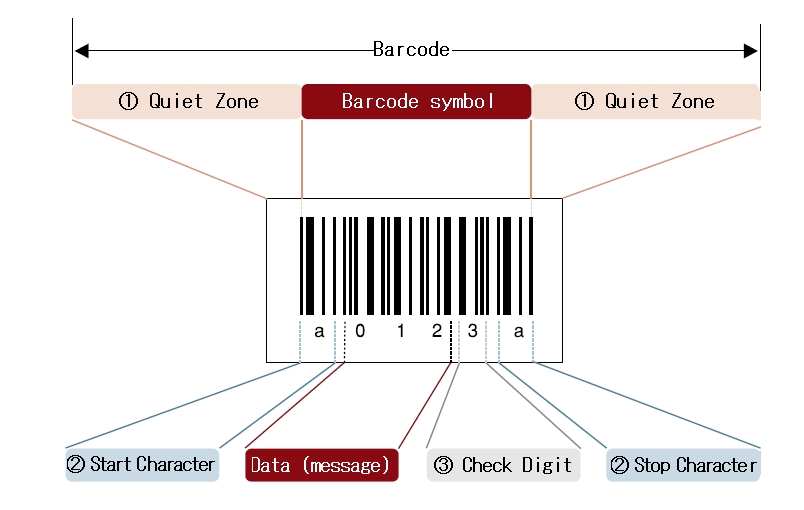
A barcode is a machine-readable code consisting of bars and spaces of varying widths, often accompanied by numbers or characters. It serves as a unique identifier for products, people, or locations. It is typically in the form of parallel lines (1D barcodes) or square dots (2D barcodes like QR codes). When scanned, it retrieves stored information such as product IDs, prices, or batch numbers
Why Use a Barcode?
Barcodes offer several benefits for businesses:
- Increased Accuracy: Barcodes eliminate manual data entry errors, ensuring precise information transfer for inventory management, sales tracking, and order fulfillment.
- Real-time Data Tracking: Each scan updates the system instantly, providing accurate stock levels and aiding in better decision-making for restocking, promotions, and inventory control. This reduces the risk of overstocking or understocking.
- Cost Savings: Automating data collection reduces the need for manual labor, saving time and money. In warehouses, barcode systems speed up inventory management and boost productivity.
Which Industries Need Barcodes?
Barcodes are used across a wide range of industries.
- Retail: In retail, they are essential for inventory management, sales tracking, and the checkout process. Retailers rely on barcodes to keep track of stock levels, manage product pricing, and provide customers with accurate receipts.
- Healthcare industry: Barcodes are used to label medications, medical devices, and patient identification bands. This ensures patient safety by preventing medication errors and enabling accurate tracking of medical supplies.
- Warehousing and logistics: Barcodes on packages and pallets act as digital signposts, allowing for precise inventory tracking. They help in making the most of storage space and guaranteeing that deliveries are made on time. Shipping companies can use these barcodes to update customers on the location of their packages at every step of the journey.
- Manufacturing: By labeling components with barcodes, they can trace the origin, production history, and quality status of each part. This is crucial for quality control and troubleshooting on the production line.
- Marketing: QR codes, a type of 2D barcode, can be placed virtually anywhere, whether within a business or on promotional materials like flyers and posters. When scanned, these codes can direct people to web pages or prompt app downloads. Companies can use them to link to their websites or social media pages, where all the relevant marketing information that might not fit in a printed ad can be accessed, thereby enhancing brand engagement and customer reach.
Types of Barcodes
There are two main types of barcodes: 1D (Linear) Barcodes and 2D Barcodes. Linear barcodes are the most common and are what most people picture when they think of a barcode. They consist of a series of parallel lines and spaces and are used for basic product identification. Examples include the UPC and the European Article Number (EAN).
Two - dimensional (2D) barcodes, on the other hand, can store much more information. They are commonly used for more complex applications, such as storing URLs, contact information, or multimedia. Examples include QR Codes, Data Matrix, MaxiCode, and GS1 DataMatrix. These barcodes are ideal for applications requiring larger data storage, such as marketing campaigns, payment solutions, or customer engagement.
How to Create a Barcode System for Your Business?
A barcode system consists of three main components: a database, a printer, and a scanner. Here is a step-by-step guide for you to get started.
Create Barcodes and Database
We have introduced how to create a barcode in previous article. Barcodes can be created for internal use (e.g., warehouse tracking) using free online generators, which quickly produce custom barcodes from product IDs or batch numbers. For global distribution, products need GS1 registration to obtain a unique company prefix, ensuring recognition across supply chains. High-volume businesses may benefit from dedicated software or ERP integrations for automated, bulk barcode generation.
A barcode database links barcodes to essential product information, such as name, price, inventory levels, and supplier details. Scanning the barcode retrieves this data, aiding tasks like inventory updates, sales tracking, and compliance management.
Choose a Barcode Printer
When choosing barcode printers, two main factors come into play: technology and type.

1. Printer's Technology
- Inkjet Printers: Inkjet printers work by spraying ink onto the printing surface. They are relatively cost - effective for small - scale and short - term projects. They can print on a variety of materials, including paper, plastic, and some fabrics. However, the print quality may not be as high as laser printers, and the ink can be prone to smudging. Also, inkjet printers may be slower in high - volume printing compared to other options.
- Laser Printers: Laser printers use a laser beam to create an electrostatic image on a drum, which then attracts toner to form the barcode. They offer high - resolution prints, which are great for barcodes that need to be scannable from a distance or in challenging environments. Laser - printed barcodes are more durable and less likely to smudge compared to inkjet prints. But laser printers are generally more expensive upfront, and the cost of toner cartridges can be high over time.
2. Printer's Type
- Large (Stationary) Printers: Large barcode printers are designed for high - volume production. They are often used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing plants and large warehouses. These printers can handle continuous printing tasks, print at high speeds, and can be integrated into automated production lines. They usually have a larger paper or label capacity, reducing the need for frequent refills. However, they are bulky, require a dedicated space for installation, and are more expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Portable/Handheld Printers: Portable or handheld barcode printers are extremely convenient for on - the - go applications. Retail employees can use them for inventory checks on the sales floor, and delivery drivers can print barcodes for packages while in the field. They are lightweight, battery - powered (in most cases), and easy to operate. But they have a smaller print capacity compared to large printers, may not be able to print as fast, and the print quality might be slightly lower. Their battery life can also be a limiting factor for extended use.

Choose a Scanner
Before choosing a scanner, consider the types of barcodes you need to scan:
- For 1D barcodes, a laser scanner is often sufficient. It's inexpensive, reads codes up to two feet away, and works with most 1D formats.
- For 2D barcodes, opt for an imager scanner. It captures images with a camera and reads both 1D and 2D codes, handling more complex formats.
Also, factor in the environment:
- In industrial settings, choose a rugged scanner that can endure drops, dust, and moisture.
- In retail, a lighter, user-friendly scanner may be better.
Ensure the scanner integrates well with your existing systems for smooth data communication.
In Conclusion
Barcodes are an essential technology in today's business world. They offer numerous benefits, from improving efficiency and accuracy in business operations to enhancing the customer experience. Understanding the different types of barcodes, how to create a barcode system, and how to choose the right barcode printers and scanners is crucial for businesses of all sizes. By implementing an effective barcode system, businesses can gain better control over their inventory, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity.
Ask Question
No questions and answers

