Barcode vs QR Code 101: Information You Need to Know
Barcodes and QR codes are two types of machine-readable codes, that widely used across industries in today's digital world. They have different applications, but both QR codes and barcodes serve the same primary purpose: to make storing and accessing data easier. Understanding the differences between these two types of codes and choosing the right one for your business can significantly optimize operations and enhance the overall customer experience.
What is a Barcode?
A barcode is a machine-readable image designed to encode information in a visual format that can be quickly scanned and interpreted by devices. It is composed of patterns such as black bars and white spaces (linear barcodes) or geometric shapes like dots and rectangles (matrix or 2D barcodes). These patterns encode information such as product identifiers, serial numbers, or tracking data, which can be scanned and interpreted by specialized devices or mobile applications.
How does Barcode Work?
The barcode is simply an image. To become meaningful, a barcode reader, or scanner, must decode it. The scanner emits a light beam, usually a laser, onto the barcode, where the black bars absorb the light and the white spaces reflect it. Then the scanner converts the reflected light into an electrical signal, representing the specific information encoded in the barcode. Decoding software processes the signal and translates it into digital data, such as a product ID or serial number, which is sent to a computer or system for action, like recording a sale or updating inventory. This process ensures quick and accurate data retrieval, and is widely used in various scenarios such as warehousing and sales.

What is a QR Code?
A QR code (short for Quick Response code) is a grid of black and white squares or pixels that encodes data in a format readable by machines. It is the most common type of 2-D barcode. By scanning a QR code with a smartphone or camera, users can quickly access the stored information such as numbers, website URLs, photographs, fingerprints, signatures, or other types of data, making it a fast and efficient way to share data.
How does QR Code Work?
A QR code works by being scanned with a device like a smartphone or QR scanner, which captures its image and decodes the data using specialized software. The software reconstructs the embedded information, such as URLs, text, or other data formats, even if the code is partially damaged. Once decoded, the device prompts the user to act on the information, such as visiting a website, connecting to Wi-Fi, or displaying text. This process ensures quick and efficient access to a wide variety of data.
Difference Between Barcode and QR Code
Although barcodes and QR codes are both machine-readable symbols used to store and transmit data, they differ significantly in appearance, advantage and use cases.
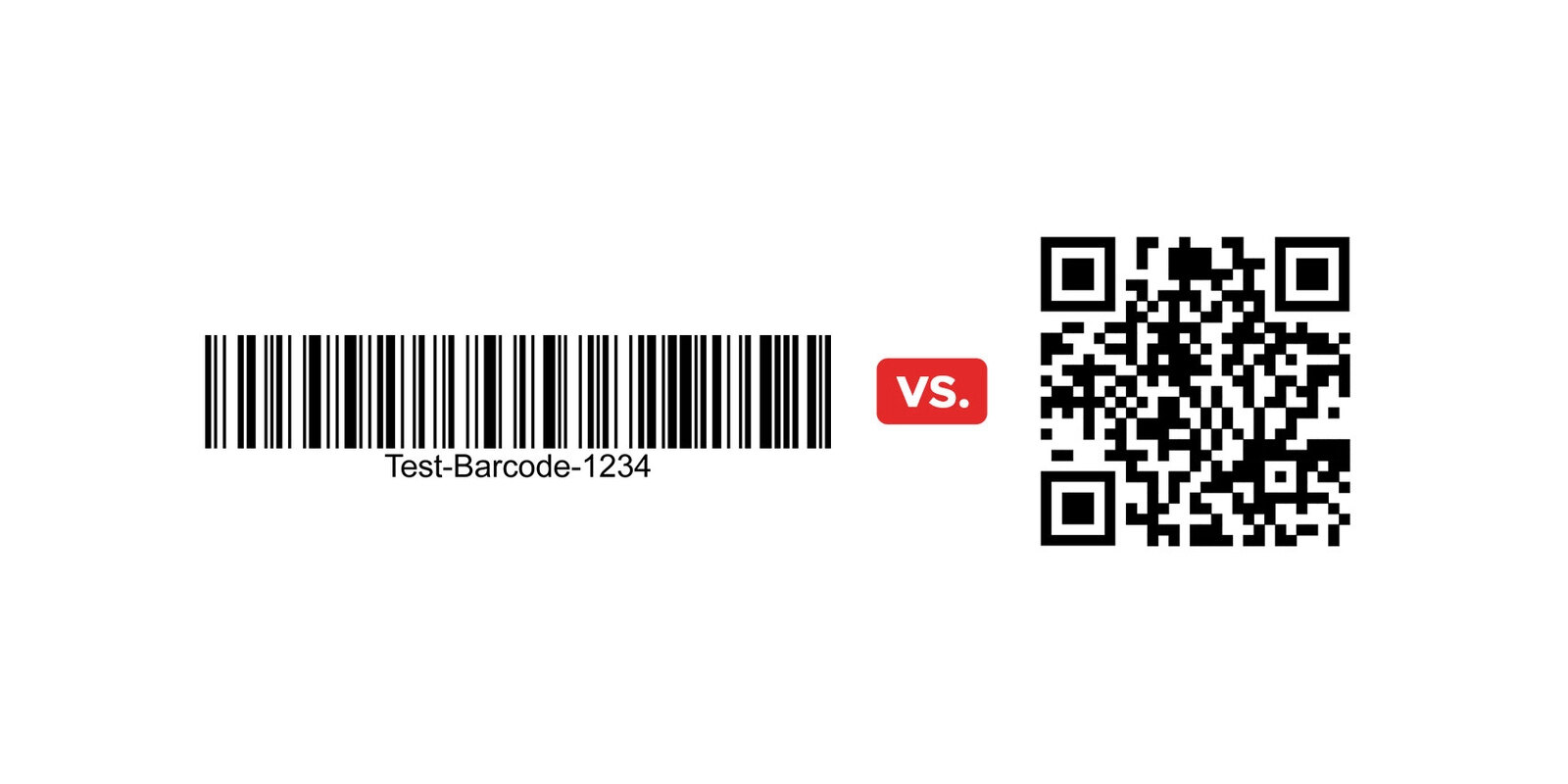
1. Appearance Differences
- Barcodes: Traditional barcodes are one-dimensional (1D) images made up of parallel black bars and white spaces. The data is encoded along a single horizontal line, and the length and width of the bars vary to represent different values.
- QR Codes: QR codes are two-dimensional (2D) images made up of a grid of black and white squares. The data is encoded in both the horizontal and vertical directions, allowing for much greater data storage capacity. They also typically include alignment markers (three large squares) to help scanning devices correctly interpret the code's position.
2. Advantages Differences
- Barcodes: Barcodes are relatively simple to generate, making them cost-effective and efficient for applications where minimal data storage is required. They are compact and do not take up much physical space, which is ideal for labeling products and packages. They work well for tracking products, inventory, and simple identifiers.
- QR Codes: QR codes can store much more data than barcodes, including URLs, contact information, and even multimedia. They offer faster scanning due to their 2D structure, and their error correction feature allows them to be read even if damaged or partially obscured. In addition to barcode scanner, QR codes can be scanned with mobile devices, making them much more versatile and user-friendly compared to barcodes.
3. Application Scenario Differences
- Barcodes: Barcodes are commonly used in retail, logistics, and manufacturing for tracking products, managing inventories, and processing sales transactions. Their simplicity (simple generation and usage) makes them ideal for environments where high-speed scanning of products is needed.
- QR Codes: QR codes are widely used in marketing, payments, and digital engagement. They are often placed on promotional materials, product packaging, or business cards to provide easy access to websites, payment links, or additional content. QR codes are also used in event ticketing, mobile payments, and information sharing, offering a higher level of interaction and versatility.

Which Code and Printer is Better for Your Business?
Both barcodes and QR codes are widely used for data encoding, each offering distinct advantages. The decision between using a barcode printer or a QR code printer largely depends on your industry, business requirements, and the type of data you need to store and track. So, which printer is best for you?
If you're in the industries of Retail, Logistics and Warehousing, or Manufacturing, a barcode printer is recommended. These industries typically require encoding basic data such as prices, batch numbers, or dates. Barcodes meet these needs with ease, offering a simple and space-efficient solution that is easy to print and scan on products or packages.
On the other hand, if you need to combine multiple types of information or engage directly with customers, a QR code printer is the ideal choice. QR codes are more advanced than traditional barcodes, capable of storing a large amount of data, including URLs, contact information, payment details, and even multimedia. They can be printed on product packaging to provide customers with quick access to additional details or personalized services. QR codes also play a significant role in mobile payment solutions, event management, and consumer interactions such as appointments or bookings. QR code printers are perfect for businesses that want to offer digital content, detailed product information, or enhanced customer engagement.
Ultimately, the choice between barcode and QR code printers depends on the specific needs of your business, the type of customer experience you want to provide, and the cost you can afford.
In Conclusion
Barcodes and QR codes are essential tools for modern data encoding, each serving specific business needs. Barcodes excel in simplicity and cost-efficiency, making them ideal for inventory tracking and sales transactions in industries like retail and logistics. On the other hand, QR codes offer greater versatility, with the ability to store more complex data such as website addresses and picture, which greatly help for customer engagement in marketing, payments, and mobile applications.
Choosing between barcode printers and QR code printers depends on your business's data storage needs, industry demands, and customer interaction goals. Both of them enhance operational efficiency, so selecting the right one can significantly improve your business processes.
Ask Question
No questions and answers

